
The difference between ITSM and ESM lies mainly in their scope and application within the organization: while ITSM (IT Service Management) focuses on designing, delivering, and optimizing services specifically related to the Information Technology (IT) area, ESM (Enterprise Service Management) extends those same service management principles and best practices to the entire company, applying them to departments such as Human Resources, Finance, Customer Service, or Facilities.
ESM inherits and expands the structured approach of ITSM beyond IT to create comprehensive and consistent service management across all business areas.
Table of Contents
Introduction to ITSM and ESM
To understand the differences between ITSM (IT Service Management) and ESM (Enterprise Service Management), first, it is necessary to understand their impact on service management, problem management, and keep in mind the digital transformation strategy the company has.
Both approaches share a common methodological base—generally supported by frameworks like ITIL—and pursue the same goal: offering internal services efficiently, in a structured way, and aligned with the business. However, their main difference lies in the scope.
While ITSM focuses on optimizing IT department services, structuring processes such as incident management and problem management, ESM extends that model to the entire company, applying it to areas like Human Resources, Finance, or Purchasing.
ITSM professionalizes technology management, and ESM extends that service management logic to the entire organization.
What Is ITSM (IT Service Management)?
ITSM (IT Service Management) is a structured model for IT service management. Its purpose is to ensure that technological services are aligned with business needs, offering quality, continuity, and constant improvement.
It refers to all activities, processes, policies, assets, and resources used by an organization to provide IT service to its customers and employees, delivering maximum value. ITSM is based on ITIL best practices and articulates key service management processes, including incident management, problem management, change management, asset management, and service level management (SLAs).
The IT department functions as an internal service provider and applies methodologies to reduce interruptions, optimize resources, and improve user experience.
Its goal is to improve IT service quality, increase user satisfaction, and contribute maximum value.
What Is ESM (Enterprise Service Management)?
ESM (Enterprise Service Management) expands ITSM principles and best practices to the entire company, moving beyond focusing exclusively on the IT department. Instead of limiting service management to the technological scope, this approach also applies to areas such as Human Resources, Finance, Purchasing, User Support, or any department providing internal services.
In this way, processes such as request management, administrative approvals, or internal workflow definition are structured under a standardized, measurable, and automatable model. All departments adopt a common service delivery logic, with clear processes, defined times, and continuous tracking.
Thanks to this transversal approach, ESM becomes a true enabler of organizational digital transformation. By unifying processes and eliminating departmental silos, it fosters collaboration between areas, optimizes operational efficiency, and significantly improves employee experience.
The goal of ESM is to establish a unified service management model throughout the organization, aligning people, processes, and technology to offer more agile, coherent, and user-oriented internal services.
Use Cases of ESM in Different Departments
Some use cases where a company could apply the ESM approach in its departments:
- HR can apply service management for employee onboarding.
- Finance can structure expense approval requests.
- Facilities can manage maintenance incidents with automated flows.
- Marketing can manage internal campaign requests, content approval, or coordinate launches with other departments.
- Legal can review requests, validate contracts, and consult internal regulations.
- Purchasing can track and approve purchase orders and manage supplier requests.
ESM turns service management into a transversal organizational model, aligned with corporate digital transformation, improving employee experience and global efficiency.
Five Key Differences Between ITSM and ESM
There are several notable differences in both methodologies; here are some of them.
1. Scope and Application
ITSM specializes exclusively in IT service management within an organization, improving how technology departments provide support and solutions to customers and users.
On the other hand, ESM extends this approach beyond IT, covering all business services and establishing a unified model for service delivery throughout the company.
Conclusion: While ITSM is limited to the technological scope, ESM seeks comprehensive service management in all company areas, promoting greater efficiency and operational cohesion.
2. Objectives
IT Service Management (ITSM) has as its main purpose aligning technological services with company needs, ensuring that IT solutions generate a positive impact and add value to the organization.
For its part, Enterprise Service Management (ESM) seeks to optimize efficiency and consistency in service delivery throughout the organization, promoting integration and collaboration between different departments.
Conclusion: While ITSM focuses on maximizing the value of IT services within the company, ESM expands this focus to improve service delivery in all areas, creating a more efficient and aligned structure.
3. Processes and Practices
In ITSM, multiple structured frameworks like ITIL, COBIT, or ISO 20000 have been developed to standardize management.
ESM takes these same frameworks and applies them to different company areas, leveraging experiences gained in IT to optimize service management in other areas of the organization.
Conclusion: While ITSM is limited to process management within the IT area, ESM expands its application to standardize and improve service delivery in all departments, promoting a more efficient and centralized approach.
4. Focus on User Experience
IT Service Management (ITSM) focuses on improving user experience within the technological scope, ensuring fast response times and efficient management of incidents and requests to optimize IT support.
For its part, Enterprise Service Management (ESM) extends this focus to the entire organization, offering more agile, accessible, and personalized services in different departments, such as Human Resources, Customer Service, and Sales, improving the overall experience of employees and customers.
Conclusion: While ITSM prioritizes user satisfaction in the IT environment, ESM adopts a broader vision, improving service delivery in all company areas and strengthening operational efficiency as a whole.
5. Benefits
ITSM Management frameworks focus on IT Service to ensure comprehensive information technology management in an organization. The main benefit of this comprehensive management is the contribution of value to the organization through the use of information technologies.
For its part, ESM leverages concepts applied in ITSM to drive operational efficiency in other areas of the organization, beyond the IT area, promoting a unified service culture throughout the company.
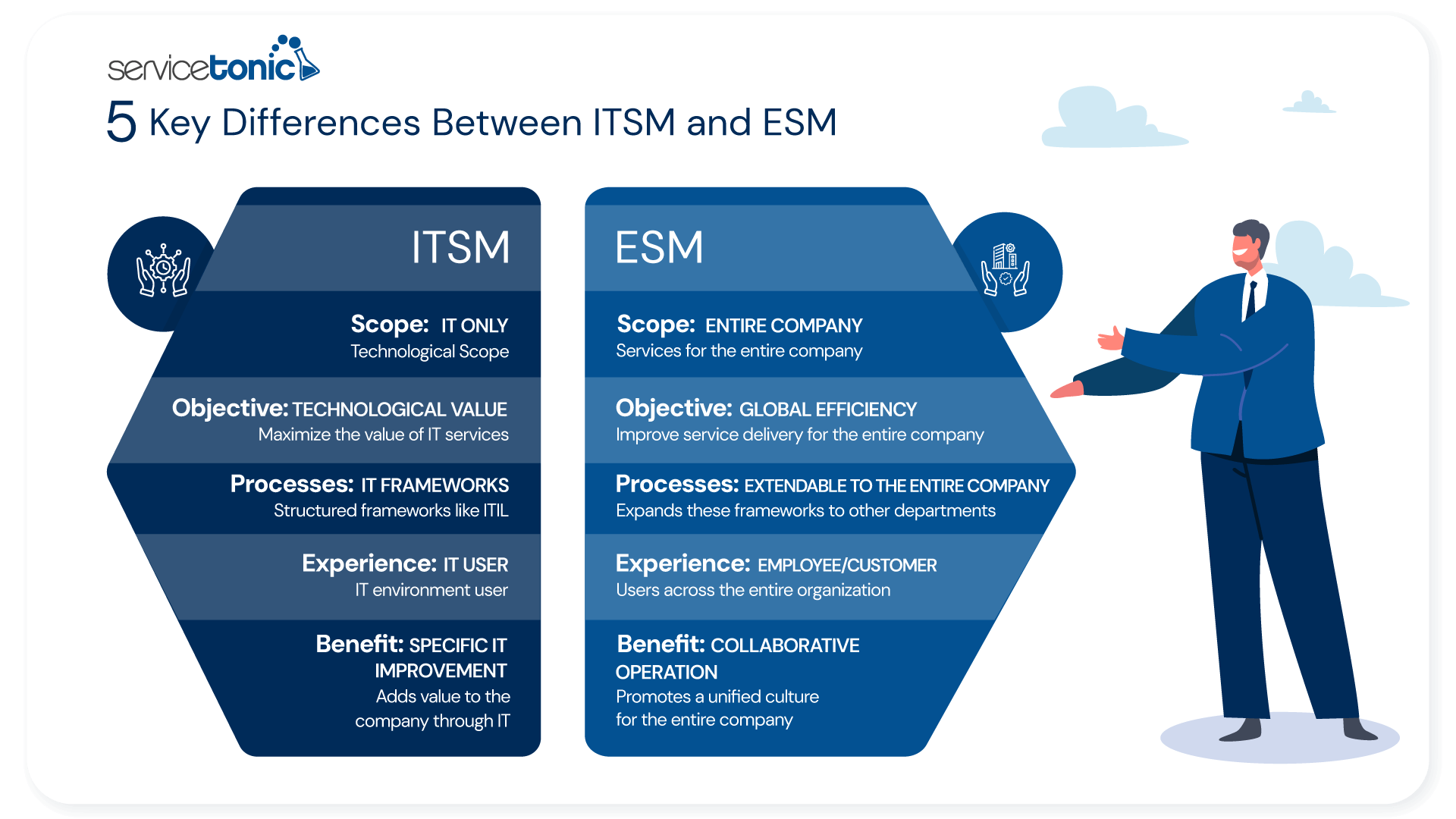
Conclusion: ITSM and ESM are totally complementary; while ITSM contributes specific improvements in IT management, ESM expands the benefits provided by ITSM to all company areas, contributing to a more efficient and collaborative operation.
Implementation of ITSM and ESM with ServiceTonic
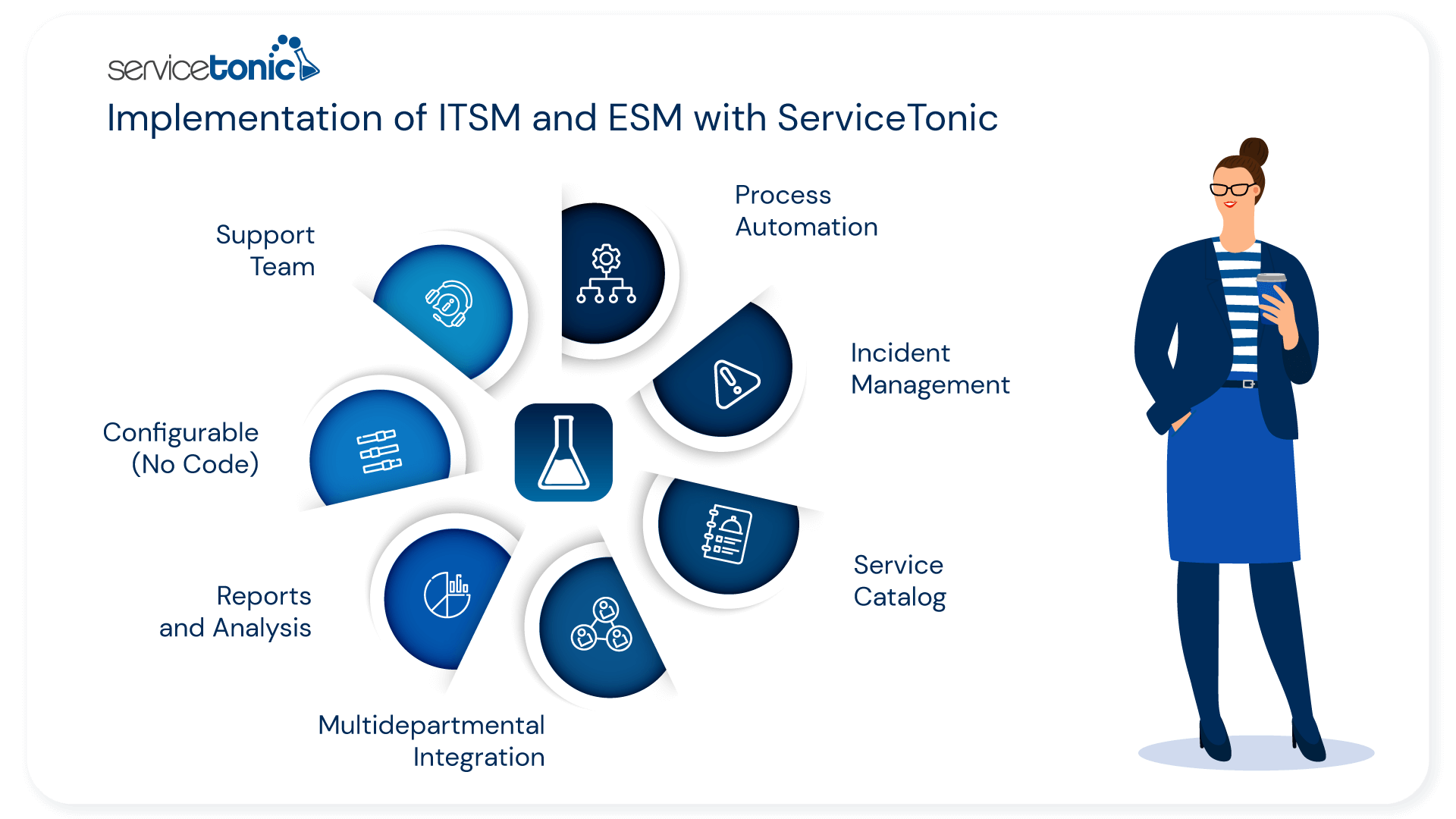
ServiceTonic is a service management solution that allows organizations to implement ITSM and ESM efficiently. Its flexible and customizable platform adapts to the specific needs of each company, facilitating process automation and improving service delivery quality.
Main features of ServiceTonic:
- Process automation: Optimizes workflows, assignments, and approvals, reducing errors and increasing operational efficiency.
- Incident and request management: Centralizes incident and request administration to ensure fast and effective responses.
- Service catalog: Allows users to easily access a customizable service catalog, ensuring a simpler and more transparent experience.
- Multi-departmental integration: Improves collaboration between different departments, achieving unified service management throughout the organization.
- Reports and analysis: Offers monitoring and analysis tools that allow evaluating performance and detecting improvement opportunities in service delivery.
- Highly configurable without programming: Its high configuration capacity allows the software to adapt to all needs of all types of companies and departments, without the need for programming knowledge.
- Great support team: Count on an excellent team of professionals who will accompany you from day one, configuring ServiceTonic to your requirements, to the day-to-day providing solutions to all types of inquiries.
With ServiceTonic, companies can optimize their IT service management through ITSM and expand these principles to other areas with ESM, achieving comprehensive and efficient management of their operations.
Conclusions
IT Service Management (ITSM) and Enterprise Service Management (ESM) have evolved as key approaches to optimize service delivery within organizations.
While ITSM focuses on efficiency within the IT scope, ESM expands these principles to the entire company, promoting a comprehensive service culture and greater collaboration between departments.
ServiceTonic presents itself as a versatile and customizable solution that allows organizations to implement both approaches efficiently. Its capacity for automation, integration, and analysis helps improve service management and optimize processes, which translates into a better experience for users and employees.
To apply ITSM and ESM, companies must evaluate their specific needs and objectives.
ITSM will help optimize your IT management, and ESM will help you expand the benefits achieved by ITSM to the rest of the areas of your organization.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the main difference between ITSM and ESM?
ITSM focuses on IT service management, ensuring that technologies are used efficiently within the organization. ESM, on the other hand, extends these principles to all departments, unifying service delivery throughout the company.
2. What are the benefits of implementing ITSM in an organization?
ITSM improves efficiency in IT management, optimizes service quality, reduces operational costs, and ensures a better user experience by streamlining the resolution of incidents and requests.
3. Why should a company consider implementing ESM?
ESM allows companies to improve efficiency and collaboration between departments, offering a unified service experience and optimizing key processes in different areas such as Human Resources, Finance, Customer Service, and Maintenance.
4. Is it difficult to implement ITSM or ESM in a company?
Not necessarily. Implementing ITSM or ESM can be simple if you have the right tool and a structured plan. ServiceTonic facilitates this process by offering a flexible and customizable platform that allows companies to adapt service management to their specific needs.
5. How can ServiceTonic help a company implement ESM?
ServiceTonic offers flexible and customizable tools for process automation, centralized request management, and report generation and analysis, facilitating the adoption of an ESM model throughout the organization.
